
![]()
Correct charging is one of the most important factors to consider when using valve regulated lead
acid batteries. Battery performance and service life will be directly affected by the charging methods.
There are four major methods of charging.
Constant voltage charging.
Constant current charging.
Two stages constant voltage charging. Taper current charging.
![]()
This is the recommended method of charging for VRLA batteries. It is necessary to closely control
the actual voltage to ensure that it is with the limits advised.
Standby service:
2.23-2.30 vpc at 20℃(68℉) to 25℃(77℉)
Cycle service:
2.40-2.50 vpc at 20℃(68℉) to 25℃(77℉)
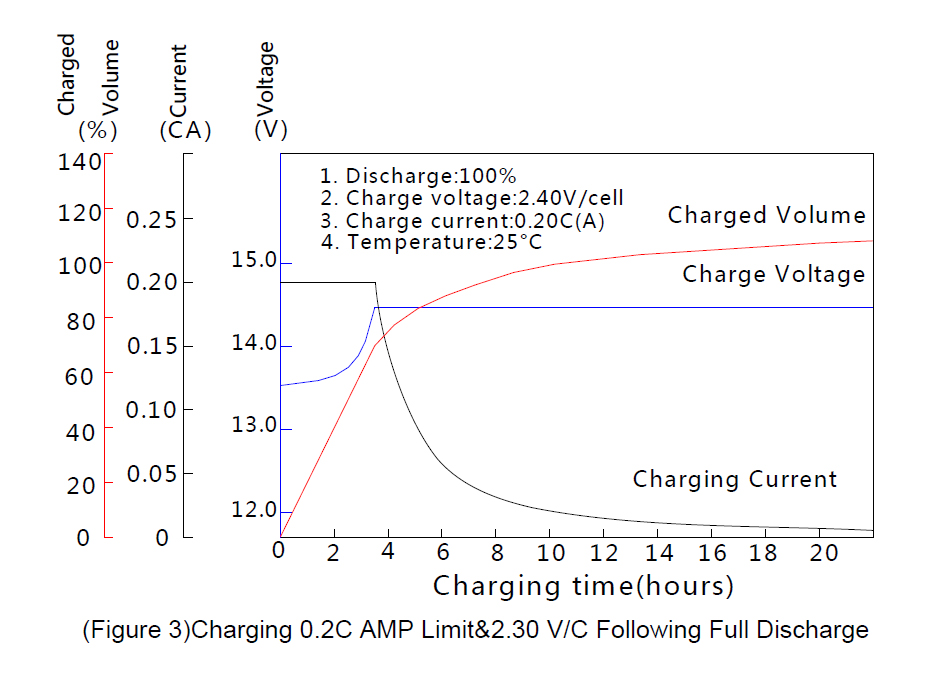
It is suggested that the initial current be set within 0.4CAmps. Figure 3 indicate the time taken to fully
recharge the battery. It is also seen that the charging current is decreased to approx 0.5-4mA/Ah
under charging voltage 2.30 vpc, and 3-10mA/Ah under charging voltage 2.40vpc when the battery is
fully charged at 20℃(68℉) to 25℃(77℉).
Note: it is necessary to ensure that the voltage is correctly set. The charging voltage set too high will
increase the corrosion of the positive plates causing loss of capacity and ultimately shortening the
life of the battery.
![]()
This method of charging is generally not recommended for VRLA batteries. It is necessary to
understand that if the batteries are not removed from the charger as soon as possible after
reaching a state of full charge. Considerable damage will occur to the batteries due to over
charging. The required recharged capacity is 1.07 to 1.15 times as discharged capacity.
![]()
This method should not be used where the battery and load are corrected in parallel, however, if this
method is to be used, it is suggested that the Sunnypower technical department be contacted.
![]()
This method is not recommended for VRLA batteries, however, if this method is to be used it is
suggested that the Sunnypower technical department be contacted.
![]()
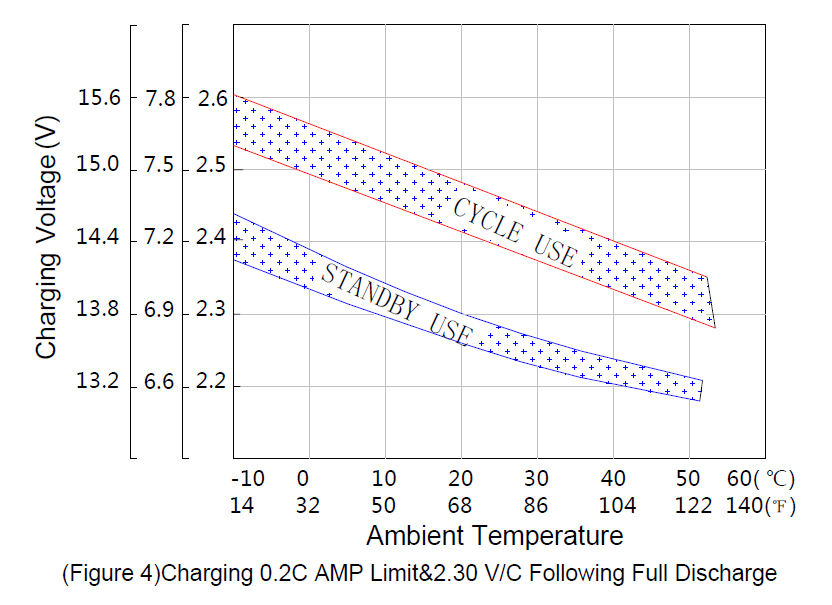
As temperature rises, electrochemical activity in the battery increases. Similarly, as temperature falls,
electrochemical activity decreases. Therefore, as temperature rises, charging voltage should be
reduced to prevent overcharge, as temperature falls, charging voltage should be increased to avoid
undercharge. In general, to assure optimum service life, use of a temperature compensated charger
is recommended. The recommended compensation factor for Sunnypower VRLA batteries is ±3mV/℃
Cell (standby use) and±4mV/℃ cell(cyclic use). The standard central point for temperature
compensation is 20℃/68℉.
Figure 4 shows the relationship between temperatures and charging voltages in both cyclic and
standby applications.
![]()
The time required to complete each charge depends on the discharge condition of battery,
characteristics of charge used, or the temperature during charge. For cyclic use, using
constant voltage charging, this time can be estimated by the following expression at 25℃/77℉.
(1)Discharge current: Larger than 0.25CA
Tch = Cdis/I + 3 ~5
(2)Discharge current: Less than 0.25CA
Tch = Cdis/I + 6 ~10
Tch: time required for charge (hours)
Cdis: ampere-hour discharged before
charge started(Ah)
I : initial charging current(A).
Complete charge time for float service will be slightly more than 24 hours.
Note: The minimum recharge capacity should be 1.02~1.05 times of discharge capacity